There are pros and cons for each loan term. We will analyze a 30 year fixed and a 15 year fixed.
A simple rule of investing, the shorter the duration of the loan (term), the lower the interest rate. This applies if all other elements are equal (loan amount, same borrower).
So, if the same borrower is offered the same loan amount for 5 years Vs. 40 years, which term would have the lower rate? The 5 year. Why? Present value of money.
Now lets do a real life example, a 30 year fixed compared to a 15 year fixed.
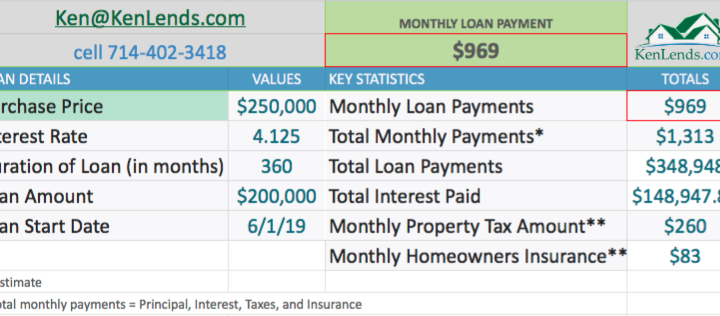
30 Year Fixed Rate Mortgage
15 Year Fixed Rate Mortgage
What do you notice about the two choices?
- Different interest rates- the 30 year is 4.125% while the 15 year is 3.75%.
- Different monthly payments- the 30 year is $1,313, while the 15 year is $1,798.
Here is the most often outcome
- The first time homebuyer or move up buyer want to qualify for the maximum. What do I mean by maximum? These borrowers would like the maximum mortgage payment underwriting will allow. For many borrowers this will be around 45% of their gross income. In some cases it may be less or more than 45%. I am using 45% for illustration purposes. Lets assume the borrower has a car loan of $100 per month, and a credit card of $25 per month.
Could the borrower qualify for the 30 year fixed rate mortgage?
- Gross Household Income: $3195
- PITI mortgage payment $1313 (PITI) and other debt of $125
- Debt to income ratio 45%
Answer: Yes. The borrower is at the maximum debt to income ratio allowed (45%)
Could the borrower qualify for the 15 year fixed rate mortgage?
- Gross Household Income: $3195
- PITI mortgage payment $1798 and other debt of $125
- Debt to income ratio 60%
Answer: No. The debt to income ratio is too high (60%).
The borrower might want the lower interest on the 15 year fixed rate mortgage. Who wouldn’t, right? But, this borrower does not qualify for the mortgage payment of the 15 year fixed rate mortgage. The borrower could use the 15 year fixed rate loan. But, the loan amount would have to be much smaller. In all likelihood, it would be difficult to find a home for the family in the lower price range. So, the borrower chooses the 30 year fixed rate option.
Where I see borrowers taking advantage of the lower rates offered with the 15 year fixed rate loan
- Wealthy– easily qualify for a 30 or 15 year loan
- Rental property with large equity– rental income of $5,000 per month with a mortgage payment of $1798. Home value of $500,000 with loan balance of $200,000.
- Conservative borrowers– anyone who wants to strategically eliminate debt and invests conservatively.
TIP: How to turn your 30 year fixed rate loan into a 15 year payoff
- Use the example above. Due to debt to income, you must take the 30 year fixed rate loan. But, you want to pay off the loan in 15 years. Every month pay an additional $523. Here is the breakdown.
If you have any questions you do not know how to answer? Contact me for help by clicking here. Or, hit me up on social media.
Facebook or Twitter: @KenLends1
Ask me any real estate or mortgage question. If you are thinking of purchasing a home, refinance, or turn home equity into cash, I can help with the process. Click this link, Contact me today.